About
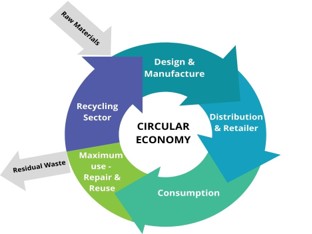
What is Circular Economy (CE)
A circular economy entails gradually decoupling economic activity from the consumption of finite resources
and is based on three principles: design out waste and pollution, keep products and materials at their
highest value and in use, and regenerate natural systems.
It leads to the transition from the current “take, make and dispose” extractive industrial model to a
decoupling of economic activity from the consumption of natural resources and designing negative
externalities such as waste and pollution out of the system.
What are the Challenges?

Natural Resources
In 2015, Asia and the Pacific represents 63% of global material use
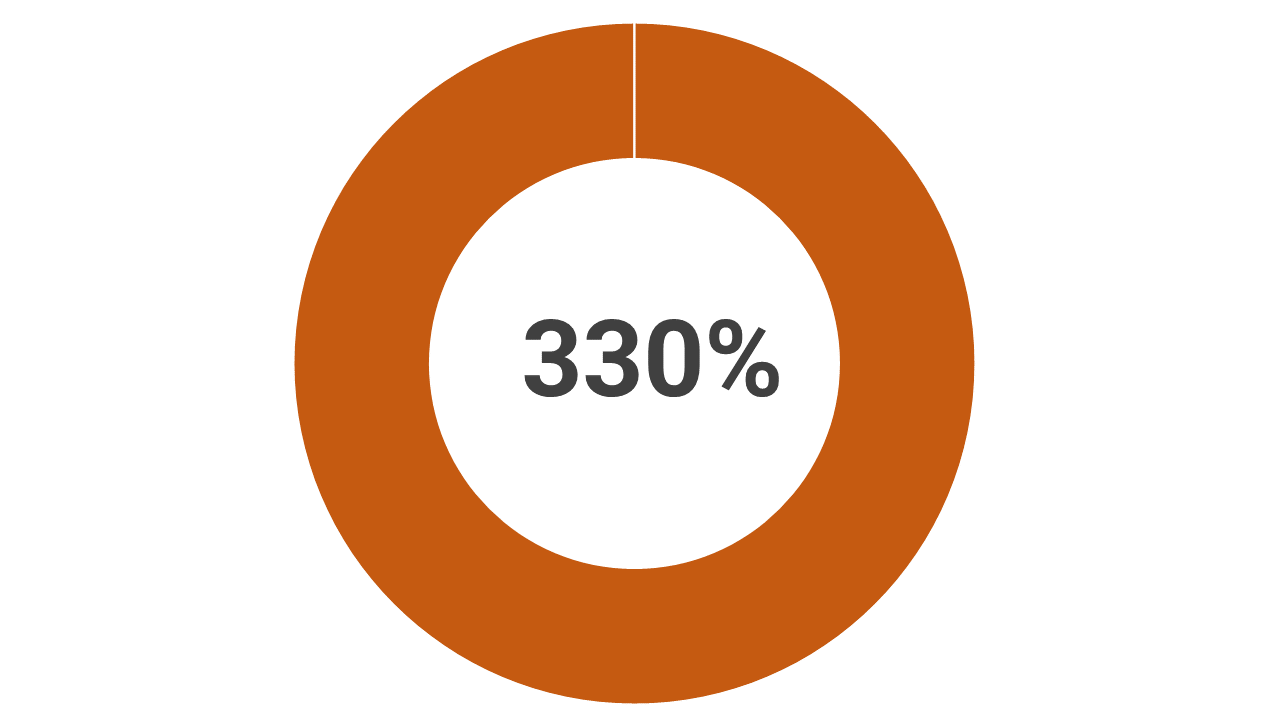
GHG emissions
GHG emissions from the region grew by 330%, including increase in short-lived climate pollutants
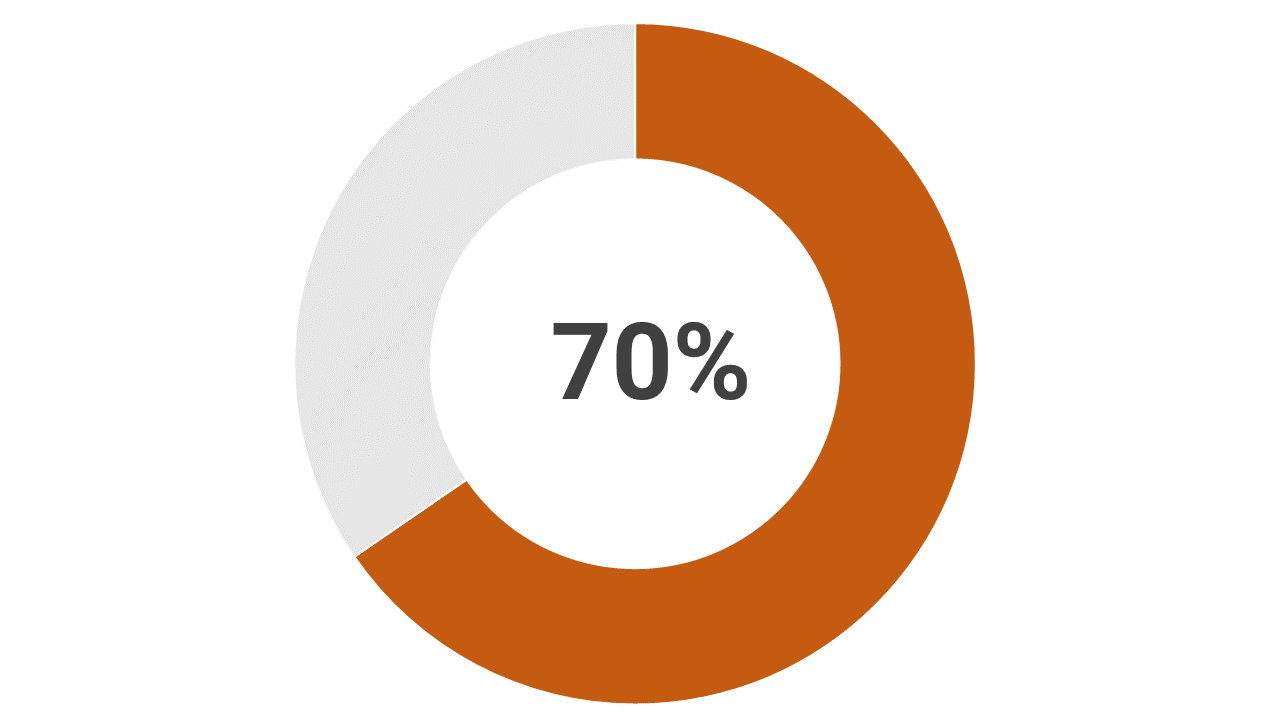
Pollution
Air pollution is responsible for more than 6.5 million deaths annually, the bulk of which – 70 %– occurs in Asia Pacific.
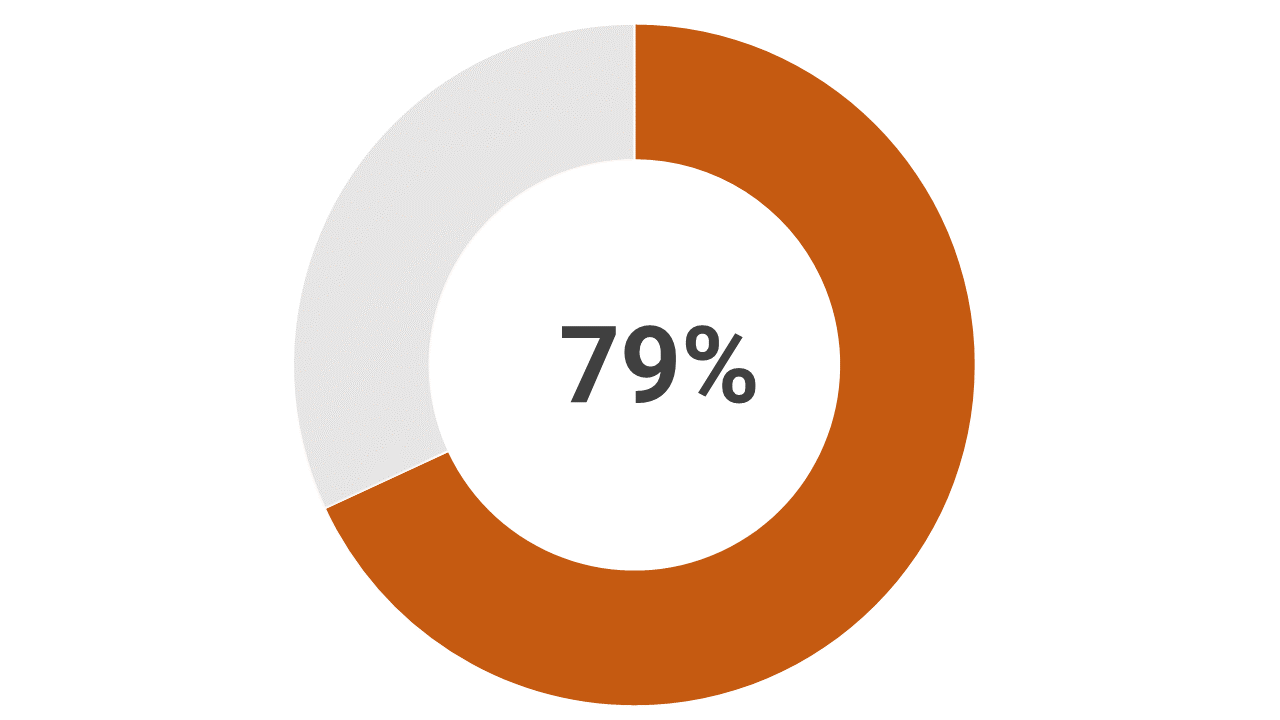
Plastic
6,300 Mt of plastic waste generated as of 2015. Of this, 9% recycled, 12% incinerated, & 79% has accumulated in landfills or environment.
Benefits of Circular Economy
Circular economy solutions can have economic, social, and environmental co-benefits through reduced demand for natural resources, reduced emissions, job creation and fostering innovation.

Economic
Social
Environment
Essential elements of Circular Economy
UNEP is leading on SDG 12 (responsible consumption and production) which provides the perfect mixture of downstream and upstream indicators for circular economy to close the loop as local as possible in the most environmentally and economically efficient manner with social benefits. As SDG 12 supports all the other SDGs, circular economy is one of the key tools to support the implementation of most of the SDGs. Based on UNEP’s comprehensive experiences, following elements need to be prioritised for circular economy:
- Integration of CE approaches and practices into policies and business decisions
- Incentive mechanisms for CE
- Market value chain and financial support to SMEs
- Stakeholders’ engagement, collaboration and Public-Private Partnerships for CE in high impact sectors
- Availability of data and replicable good practices effectively shared and replicated
- Capacity building, technical support and training for policymakers and SMEs
- Education, information and awareness for sustainable consumer choices
- Innovation and technologies for design and secondary resource extraction in supply chains
SDGs directly contributed to:

Impact
High impact sectors for Circular Economy
Electronics and ICT
- Energy efficiency, reparability, maintenance, reuse and recycling
- Devices such as mobile phones, tablets, laptops, cartridges, chargers, equipment
- Take back schemes
- Improved collection and sorting
Plastic and packaging
- Re-use and Recyclability
- Responsible use of plastic
- Eliminate single-use packaging
- Limit microplastic content
- Collection, sorting and recycling
- Use of recycled plastics
Transport
- Service based transport system Easy to use public transport
- walking, cycling, ridesharing, carsharing, alternative transport methods,
- Electric, biogas, fossil-free cars
Food systems
- Responsible consumer choices
- Food processing and retail sectors – transport, storage, packaging and food waste
- Sustainable agriculture practices
- Proper reuse of organic waste
Textiles
- Boosting market for textile reuse and sustainable textiles
- Addressing fast fashion
- Ecodesign measures
- Sustainable consumer choices
- Sorting, reuse and recycling of textiles
- Circular processes
Construction and infrastructure
- Green public procurement
- Energy and resource efficiency
- Increased recycled content and durability
- Management of Construction and demolition waste
Energy
- Renewable energy, waste-to-energy, fuel conversion, recycling materials from energy plants
- Energy efficiency
- Energy-as-a-service
- Utlisation of excess energy and side streams
Industry
- Green procurement
- Ecodesign: durability and reusability
- Material efficiency
- Digital technologies
- Sustainability reporting
- Enabling remanufacturing and high-quality recycling
- Secondary raw materials

